Research Article 
 Creative Commons, CC-BY
Creative Commons, CC-BY
Assuring Optimal Breastfeeding Practice to Prevent Adult Disease Induction: A Preliminary Report on Comparative Presentation on LATCH Score, Eregie BREAST Score (EBS) and Eregie Breastfeeding Assessment Tool Examination Score (EBATES)
*Corresponding author: Charles Osayande Eregie, MBBS, FWACP, FMCPaed, FRCPCH (UK), Cert. ORT (Oxford), MSc (Religious Education), FAMedS, FIPMD, FIMC, CMC, CMS, FRCP (Edin), Child Health and Neonatology, Institute of Child Health, University of Benin, Consultant Paediatrician and Neonatologist, University of Benin Teaching Hospital, Nigeria.
Received: October 21, 2024; Published: October 25, 2024
DOI: 10.34297/AJBSR.2024.24.003211
Abstract
Breastfeeding is a Low-cost High-impact Child Feeding Intervention which confers a myriad of Benefits on the Child-Mother Dyad. Breastfeeding, particularly Exclusive Breastfeeding, is the ‘Starting Locus’ of the Pre-FOAD Hypothesis which assures the attainment of Maternal Phenotype which, through Foetal Programming and Developmental Plasticity in a Transgenerational Model, determines the Birth Body Composition with implications for the Prevention of Adult Disease Induction (ADI). These Breastfeeding Benefits, including the Epigenetic Benefits, are guaranteed only with Optimal Breastfeeding Practice which is also only assured with the ‘Intervention’ of deploying Appropriate Breastfeeding Assessment Tools. These focus on the Breastfeeding Assessment Domains to guide Specific Interventions for Breastfeeding Practice Improvements. There are several Breastfeeding Assessment Tools with differential Advantages and Disadvantages. Three Tools with Objective Scoring Schemes were selected and evaluated: LATCH Score, Eregie BREAST Score (EBS) and Eregie Breastfeeding Assessment Tool Examination Score (EBATES). The EBATES is the Objective Scoring Scheme with the best (100.0%) Breastfeeding Assessment Domains Coverage while the LATCH Score comparatively had a Coverage of 44.4% and the EBS had a Coverage of 77.8%. With the EBATES as an ‘Intervention’, Breastfeeding Practice can be optimized to assure its Epigenetic Benefit and Prevent Adult Disease Induction with its Public Health Import. EBATES, as an Intervention, not only assures Optimal Breastfeeding as a Low-cost High-impact Child Survival Intervention but also assures the Prevention of Adult Disease Induction (ADI).
Keywords: Adult Disease Induction, Breastfeeding Assessment Domains, Breastfeeding Assessment Tools, Child Survival Interventions, Developmental Plasticity, DOHIDIMS, DOLSOC2PH3I2N2DIMS, Epigenetics, Epigenetic Mechanisms, Exclusive Breastfeeding, Foetal Programming, Maternal Phenotype, Nutritional Epigenetics, Nutrigenetics, Nutrigenomics, Pre-FOAD Hypothesis
Abbreviations: ADI: Adult Disease Induction, BAS: Breastfeeding Assessment Score, BEET: Breastfeeding Evaluation and Education Tool, BFHI: Baby-Friendly Hospital Initiative, CBF: Continued Breastfeeding; CF: Complementary Feeding, CSI: Child Survival Interventions, EBATES: Eregie Breastfeeding Assessment Tool Examination Score, EBF: Exclusive Breastfeeding, EBM: Expressed Breastmilk, EBS: Eregie BREAST Score, EIB: Early Initiation of Breastfeeding, FOAD: Foetal Origins of Adult Disease, IBFAT: Infant Breastfeeding Assessment Tool, NOMAS: Neonatal Oral-Motor Assessment Scale, OIYCF: Optimal Infant and Young Child Feeding, SIAB: Systematic Assessment of the Infant at Breast, UNICEF: United Nations Children’s Fund, WHO: World Health Organization.
Introduction
Breastfeeding is an integral component of Optimal Infant and Young Child Feeding (OIYCF) recommended by the WHO [1] and UNICEF [2] and includes Early Initiation of Breastfeeding (EIB) within the 1st Hour of Birth, Exclusive Breastfeeding (EBF) for the first 6 Completed Months of life, Introduction of Age-Appropriate Diverse and Nutritious Complementary Feeding (CF) with Continued Breast-Feeding (CBF) until 2 years or beyond if feasible. This requires the understanding of OIYCF Ecosystem and addressing all the determinant Components of the Ecosystem to assure the Protection, Promotion and Support of Breastfeeding for the benefit of the Products of Reproductive Interventions within the OIYCF Space [3]. Breastfeeding is a Low-cost High-impact Child Survival Intervention (CSI) [4] and disposes Two Conceptual Facts: ‘Breastfeeding is more than Feeding’ and ‘Breastmilk is more than Food’ [3,5-7]. These Conceptual Facts derive from understanding Breastfeeding as an Intervention with Nutritional Epigenetic Implications [8,9] and, therefore, has the potential, with influence on the Maternal Phenotype and the resultant Foetal Programming through Developmental Plasticity, to affect future Adult Disease Induction (ADI) [10] with its Public Health Import.
To assure the Nutritional Epigenetic Benefits of Breastfeeding for the Child-Mother Dyad, the Feeding Intervention must be practiced with the appropriate Skills and Techniques. This requires proper Breastfeeding Assessment and the deployment of Breastfeeding Assessment Tools, as an Intervention, to facilitate the identification of specific aspects of Breastfeeding for possible further attention and Specific Interventional Adjustments. There are several Breastfeeding Assessment Tools with different comparative Advantages and Disadvantages [11-22]. Some of these Breastfeeding Assessment Tools were disposed in previous Communications [21,22]. There is reportedly ‘No Gold Standard’ as a Breastfeeding Assessment Tool and there has reportedly been unending drive to develop and deploy Breastfeeding Assessment Tools with improved performance as ‘Interventions’ to assure ‘Breastfeeding’ as a means to prevent ADI taking cognizance of its Nutritional Epigenetic Implications [23] and the Public Health Nexus. This Communication disposes a Preliminary Report on the Comparative Presentation on three Objective Scoring Schemes for Breastfeeding Assessment as an ‘Intervention’: LATCH Score, Eregie BREAST Score (EBS) and Eregie Breastfeeding Assessment Tool Examination Score (EBATES).
Breastfeeding, Breastmilk, Exposomics and Nutritional Epigenetics
Ordinarily, Breastfeeding is the feeding of the offspring with breastmilk obtained directly by suckling at the breasts of the mother granted that Indirect Breastfeeding may also imply feeding the Offspring with Expressed Breastmilk (EBM) as a Case-in-Point. In Epigenetics and Conversational Discourse on the ‘Environment’, the Breastfeeding Suckling Practice and Exposure reportedly constitute ‘Environmental Exposures’ which initiate a plethora of various and varied Epigenetic Mechanisms which reportedly include, among others: DNA Methylation, Histone Modifications, Chromatin Re-Modelling and Non-Coding RNA Modulations with resultant Phenotype Alterations in the Structure, Functions, Metabolism and Gene Expression or Repression without the DNA Sequence Alterations [24-28]. This simply implies that Breastfeeding has implications for the resultant Phenotype without DNA Sequence Alterations; Breastfeeding is More than Feeding [3,5-7]. Breastfeeding is, therefore, reportedly part of the Exposome and Exposomics [29,30] of the Growing and Developing Human Being. The Breastmilk obtained through Breastfeeding also has contents which, reportedly beyond yielding Macronutrients and Micronutrients, also have Epigenetic Implications and, therefore, similarly impact on Phenotype Alterations without the DNA Sequence Alterations. Breastmilk is, ipso facto, also More than Food as it reportedly contains Bioactive Components which are also reportedly involved in Epigenetic Mechanisms with some of the ‘Epigenomes’ including, but not limited to: Exosome-related miRNAs, Stress Modulators which impact on Neurodevelopmental-Mental Stress Status, Immunomodulators which determine resistance to Infections and Leptin-Ghrelin which modulate Energy Balance-BMI Growth Trajectory [3,5-7,31-35]. This disposes the evolving Conceptual and Contextual Technicalization in the Nutritional Epigenetics Space and Discourse [3,5-7,35]. Nutritional Epigenetics reportedly has ‘Two Bi-Directional Components’: Nutrigenomics which is the Conceptual Discourse of the Effects of Food with its Bioactive Components on the DNA Structure, Functions, Metabolism and Gene Expression or Repression with resultant Phenotype Alterations but without DNA Sequence Alterations and Nutrigenetics which is the Conceptual Discourse of the Effects of Food on the Individual determined by the particular Genetic Make-up of the being. Therefore, Nutritional Epigenetics reportedly disposes the Nutrigenomics-Nutrigenetics Dyad with the potentiality for Precision Nutrition within the Personalized Nutrition Conversational Discourse [8,36].
Breastfeeding, Maternal Phenotype and Adult Disease Induction (DOLSOC2PH3I2N2DIMS)
Breastfeeding, particularly Exclusive Breastfeeding, has been presented as the ‘Starting Locus’ of the Pre-FOAD Hypothesis [10,37,38]. The Pre-FOAD Hypothesis conceptually disposes that ‘Exclusive Breastfeeding (EBF) assures that the female child experiences the ‘First Growth Spurt’ in the first 6 months of life and intertwined with Child Survival Interventions (CSI) [4] and optimizing the ‘Prepubertal Growth Spurt (Second Growth Spurt)’ results in a Maternal Phenotype which facilitates the desired Foetal Programming through Developmental Plasticity with the resultant Optimal Body Composition at ‘Birth’, in a ‘Transgenerational Model’, protecting against Adult Disease Induction (ADI)’ [10,37,38].
In a 2009 Inaugural Lecture delivered by this Author as the 106th Lecture at the University of Benin in Nigeria, the Adult Disease Induction (ADI) was signposted with the Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs) captured by the Acronym ‘DOHIDIMS’ reflecting: Diabetes, Obesity, Hypertension, Ischaemic Heart Disease, Dyslipidaemia, Insulin Resistance and Metabolic Syndrome [10]. With recent advances in ‘Epigenetics and Nutritional Epigenetics Research Outpourings’, this Author disposed an Acronymic re-conceptualization with ‘DOHIDIMS’ transmuting to ‘DOLSOC2PH3I2N2DIMS’ (Pronounced ‘DOLSOKFINDIMS’) now reflecting: Diabetes, Obesity, Lung Disease, Stroke, Osteoporosis, Cancers, Chronic Renal Disease, Psychiatric Disorders, Hypertension, Hypothyroidism, Hyperthyroidism, Ischaemic Heart Disease, Immune Dysfunction, Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Neuropsychiatric Disorders, Dyslipidaemia, Insulin Resistance and Metabolic Syndrome [39,40]. Exclusive Breastfeeding, with the Pre-FOAD HJypothesis, is a contributory determinant of the Maternal Phenotype which impacts on the Conceptus through Foetal Programming and Developmental Plasticity with a consequent ‘Birth Body Composition’ that possibly may Promote or Prevent Adult Disease Induction (ADI).
Breastfeeding, Breastfeeding Practice and Breastfeeding Assessments Tools
Optimal Breastfeeding endows the Child-Mother Dyad with benefits including its Epigenetic Implications and Prevention of Adult Disease Induction (ADI). These benefits are assured only with Optimal Breastfeeding Practice which is facilitated through Appropriate Breastfeeding Assessment. There are Breastfeeding Assessment Tools which have been developed to assist mothers in detecting specific ‘Breastfeeding Domains’ which require further focus and attention towards improving the Breastfeeding Practice. Some of these Breastfeeding Assessment Tools include, among others: WHO/UNICEF BFHI Forms [11,12], CARE Training Packages [13] , Breastfeeding Assessment Score (BAS) [14], Breastfeeding Evaluation and Education Tool (BEET) [15], Infant Breastfeeding Assessment Tool (IBFAT) [16], LATCH Score [17], Neonatal Oral-Motor Assessment Scale (NOMAS) [18], Systematic Assessment of the Infant at Breast (SAIB) [19], WHO/ UNICEF B-R-E-A-S-T-Feed Observation Form [20], Eregie BREAST Score (EBS) [21], Eregie Breastfeeding Assessment Tool Examination Score (EBATES) [22] etc. These Breastfeeding Assessment Tools reportedly have differential Advantages and Disadvantages and have been critically disposed in some previous Communications [21-23,41]. It is reportedly disposed that there is ‘No Gold Standard’ as a Breastfeeding Assessment Tool necessitating the continuous and on-going search for, and development of, Improved Breastfeeding Assessment Tools [21-23].
Comparative Assessments of Selected three Breastfeeding Assessment Scoring Schemes
Some Breastfeeding Assessment Tools [11-22] have been identified in this Communication without disposing their Operational Details which are presented in some other Comminications [21,22,41]. It is reportedly suggested that several ‘Breastfeeding Assessment Tools’ have various and varied Strengths and Weaknesses including but not limited to: Breastfeeding Domains Coverage, Independent Objective Validation, Universal Applicability, Objective Scoring Schemes, Quality of Study Designs, Correlation Studies with Breastfeeding Outcomes, Observable Parameters-based, Questionnaire-denominated, User-friendliness etc [23,41]. The WHO/ UNICEF B-R-E-A-S-T-Feed Observation Form [20] reportedly has many positive attributes [23,41] but lacks an ‘Objective Scoring Scheme’ [21,22]. Only one Tool, the Breastfeeding Evaluation and Education Tool (BEET) [15], reportedly had 100% Breastfeeding Domains Coverage [41] but it also lacks the Objective Scoring Scheme [21,22]. Also reportedly, lack of agreement or commonality of how best to Assess Breastfeeding using the various Tools is a difficulty with most extant Breastfeeding Assessment Tools and Exercise [41]. Therefore, three Breastfeeding Assessment Tools which were developed as Objective Scoring Schemes were selected for some Comparative Evaluations based on Critical Review of the Literature coupled with this Author’s longstanding years of Clinical Experience/ Expertise, Research and Practice of Child Health, Neonatal Medicine and Breastfeeding Medicine laced with extensive Breastfeeding Publications and National and International Programmatic Engagements and Interventions in Breastfeeding Initiatives. The selected Breastfeeding Assessment Tools are: LATCH Score [17] consisting of the ‘Breastfeeding Domains’ (Five Domains included): Latch, Audible swallowing, Type of Nipple, Comfort and Hold, the Eregie BREAST Score (EBS) [21] consisting of the ‘Domains’ (Nine Domains included): Body position (Mother and Baby), Responses (Mother and Baby), Emotional bonding (Mother and Baby), Anatomy (Mother only), Suckling (Baby only) and Time spent suckling and the Eregie Breastfeeding Assessment Tool Examination Score (EBATES) [22] consisting of the ‘Breastfeeding Domains’ (Twelve Domains included): Baby’s behavior, Mother’s behavior, Positioning (Baby and Mother), Attachment, Effective feeding (Baby and Mother), Health of the breast, Health of the Baby, Mother’s feel of feed, Mother’s level of comfort and Length of feed. In Research Governance Principles, and as a Research Strategy, the Methodology adopted for this Report is a Non-Clinical Comparative Evaluations with ‘No Contacts or Interventions’ between Patients and the Researcher as No Patient was Involved.
In Table 1, certain Attributes of the selected Scoring Schemes are disposed. The three selected Tools have some Attributes as Commonality re: Include Observable Characteristics of the Breastfeeding Baby-Mother Dyad, Easily Definable and Scored Alternatives, Universal Applicability and User-Friendliness. They also include Attachment and Effective Feeding as ‘Breastfeeding Domains’ which were reportedly ubiquitously included in virtually all previous Breastfeeding Assessment Tools [23]. The Scoring Schemes uniquely differ in their Breastfeeding Assessment Domains Coverage with the LATCH Score covering only Five Domains, the Eregie Breast Score (EBS) covering Nine Domains and the Eregie Breastfeeding Assessment Tool Examination Score (EBATES) covering Twelve Domains. For better Discriminant Functional Performance Ability, the latter two Scoring Schemes (EBS and EBATES) included Separate Assessment Domains for the Baby and the Mother in some Domains [21,22]. The Breastfeeding Assessment Domains Coverage is reportedly a determinant attribute of useful Breastfeeding Assessment Tools [23,41]. The differential Breastfeeding Domains Coverage by the three selected Objective Scoring Schemes is further disposed in Table 2 using an Evaluation Frame previously deployed for similar exercise [23,41]. The EBATES is the Objective Scoring Scheme with the best (100.0%) Breastfeeding Domains Coverage in addition to the other desired Attributes as Commonality. Comparatively, LATCH Score had 44.4% Domains Coverage while EBS had 77.8% Coverage (Table 2).
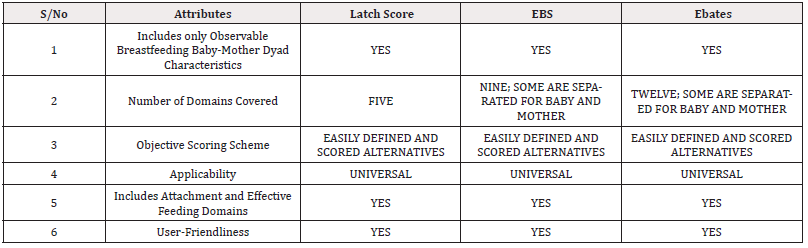
Table 1: Breastfeeding Attributes of the selected three Objective Scoring Schemes Evaluated.
Note*: KEY/ LEGEND EBS: Eregie BREAST Score EBATES: Eregie Breastfeeding Assessment Tool Examination Score.
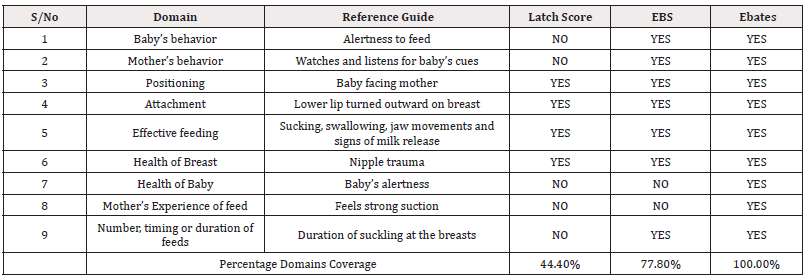
Table 2: Comparative Breastfeeding Domains Coverage of selected three Objective Scoring Schemes for Breastfeeding Assessments. Tool Assessment Table adapted from Moran VH, Dinwoodie K, Bramwell R, Dykes F. A critical analysis of the content of the tools that measure breast-feeding interaction. Midwifery 16(4): 260-268 [23]. Management of Acute Malnutrition in Infants (MAMI) Project. Chapter 7: Review of breastfeeding assessment tools. Write-up beyond the scope of the original MAMI Project and Additional Feedback from Felicity Savage and Ann Ashworth [41].
Note*: Key/ Legend EBS: Eregie BREAST Score EBATES: Eregie Breastfeeding Assessment Tool Examination Score.
Conclusion
Breastfeeding is part of the Optimal Infant and Young Child Feeding with a plethora of benefits to the Breastfeeding Child-Mother Dyad and include Epigenetic Implications. Exclusive Breastfeeding, as the ‘Starting Locus’ of the Pre-FOAD Hypothesis, contributes to determining the Maternal Phenotype which drives Foetal Programming through Developmental Plasticity, and the Transgenerational Model, to achieve the desired Birth Body Composition which shapes future Health Trajectory and the prevention of Adult Disease Induction. These Breastfeeding Benefits are only guaranteed with Optimal Breastfeeding Practice. The ‘Intervention’ that assures Optimal Breastfeeding Practice is Appropriate Breastfeeding Assessment predicated on the deployment of Useful Breastfeeding Assessment Tools. Several Tools exist with differential Advantages and Disadvantages. Three Breastfeeding Assessment Tools developed as Objective Scoring Schemes were evaluated using previously utilized Evaluation Frame disposing Breastfeeding Assessment Domains Coverage. The selected and evaluated three Objective Scoring Schemes were the LATCH Score, Eregie Breast Score (EBS) and Eregie Breastfeeding Assessment Tool Examination Score (EBATES). The EBATES is the Objective Scoring System with the best (100.0%) Breastfeeding Domains Coverage in addition to other laudable Attributes of Breastfeeding Assessment Tools. Deploying EBATES as an ‘Intervention’ assures Breastfeeding contributes to impacting on the Maternal Phenotype which ultimately prevents Adult Disease Induction with its Public Health Impact. Exclusive Breastfeeding is not only a Low-cost High-impact Child Survival Intervention, it is also a Low-cost High-impact Intervention and Strategy for the Prevention of Adult Disease Induction taking cognizance of its Nutritional Epigenetics Implications.
Conflict of Interests
None.
Acknowledgement
None.
References
- (2021) World Health Organization. Infant and young child feeding. Geneva.
- (2021) UNICEF. Infant and Young child feeding. New York.
- Eregie CO (2023) Addressing the Optimal Infant and Young Child Feeding Ecosystem to improve the Status of the Outcome of Reproductive Interventions; No ‘Breastmilk Substitutes’. Global Journal of Reproductive Medicine 10(2): 555784.
- Health Think. Child Survival Strategies: Addressing under-5 Mortality in Nigeria.
- Verduci E, Barderali G, Barberi S, Giovanni Radaelli, Alessandra Lops, et al. (2014) Epigenetic effects of Human Breast Milk. Nutrients 6(4): 1711-1724.
- Genna CW (2018) Epigenetics, Methylation, and Breastfeeding. Clinical Lactation 9(3): 144-147
- Briollais L, Rustand D, Allard C, Yanyan Wu, Jingxiong Xu, et al. (2021) DNA methylation mediates the association between breastfeeding and early-life growth trajectories. Clinical Epigenetics 13(1): 231.
- Farhud DD, Yeganeh MZ, Yeganeh MZ (2010) Nutrigenomics and Nutrigenetics. Iran J Public Health 39(4): 1-14.
- Faa G, Fanos V, Manchia M, Van Eyken P, Suri JS, et al. (2024) The fascinating theory of fetal programming of adult diseases: A review of the fundamentals of the Barker hypothesis. J Public Health Res 13(1): 22799036241226817.
- Eregie CO (2009) Programming the END from before the BEGINNING-: Juxtaposing TECHNOLOGY with the TEA Triad’ University of Benin Press. 106th Inaugural Lecture, University of Benin, Nigeria.
- Hall RT, Mercer AM, Teasley SL, Susan L Teasley, Deanna M McPherson, et al. (2002) A breast-feeding assessment score to evaluate the risk for cessation of breast-feeding by 7 to 10 days of age. J Pediatr 141(5): 659-664.
- Tobin DL (1996) A breastfeeding evaluation and education tool. J Hum Lact 12(1): 47-49.
- Matthews MK (1998) Breastfeeding assessment tools. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs 27(3): 236-238.
- Jensen D, Wallace S, Kelsay P (1994) LATCH: a breastfeeding charting system and documentation tool. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs 23(1): 27-32.
- Palmer MM, Crawley K, Blanco IA (1993) Neonatal Oral-Motor Assessment scale: a reliability study. J Perinatol 13(1): 28-35.
- Shrago L, Bocar D (1990) The infant's contribution to breastfeeding. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs 19(3):209-215.
- (1994) WHO/UNICEF: Breastfeeding counselling: a training course. World Health Organisation and United Nations International Children’s Education Fund.
- (2009) WHO/UNICEF: Baby Friendly Hospital Initiative: Revised Updated and Expanded for Integrated.
- (2010) UNICEF: Baby Friendly Hospital Initiative: Breastfeeding Assessment Form.
- (2004) CARE: Preparation of a Trainer's Course: Mother to Mother Support Group Methodology and Breastfeeding and Complementary Feeding Basics. United States Agency for International Development (USAID) / The Infant & Young Child Nutrition (IYCN) Project.
- Eregie CO (2024) Breastfeeding Assessment; Preliminary Report on a New Scoring System as an Assessment Tool: The Eregie BREAST Score (EBS). Am J Biomed Sci & Res 23(2): 241-245.
- Eregie CO (2024) Breastfeeding Assessment Tool; Preliminary Report on A Breastfeeding Domains-Based Examination Scoring System: The Eregie Breastfeeding Assessment Tool Examination Score (EBATES). Am J Biomed Sci & Res 23(4): 546-549.
- Moran VH, Dinwoodie K, Bramwell R, Dykes F (2000) A critical analysis of the content of the tools that measure breast-feeding interaction. Midwifery 16(4): 260-268.
- (2024) Wikipedia. Epigenetics.
- Yan Lin Wu, Zheng Jun Lin, Chang Chun Li, Xiao Lin, Su Kang Shan, et al. (2023) Epigenetic regulation in metabolic diseases: mechanisms and advances in clinical study. Signal Transduct Target Ther 8(1): 98.
- Li X, Wang J, Wang L, Yuanxu Gao, Guihai Feng, et al. (2002) Lipid metabolism dysfunction induced by age-dependent DNA methylation accelerates aging. Signal Transduct Target Ther 7(1): 162.
- Iyer, MK, Niknafs YS, Malik R, Udit Singhal, Anirban Sahu, et al. (2015) The landscape of long noncoding RNAs in the human transcriptome. Nat Genet 47:99-208.
- Campisano S, La Colla A, Echarte SM, Chisari AN (2019) Interplay between early-life malnutrition, epigenetic modulation of the immune function and liver diseases. Nutr Res Rev 32(1): 128-145.
- (2024) NIOSH. Exposome and Exposomics.
- (2024) HHEAR. What is the Exposome and Exposomics.
- (2019) Overview. NIH Roadmap Epigenomics Project.
- Reik W (2007) Stability and flexibility of epigenetic gene regulation in mammalian development. Nature 447(7143): 425-432.
- Moore DS (2015) The Developing Genome: An Introduction to Behavioral Epigenetics. Oxford University Press.
- Wells JC (2010) The thrifty phenotype: An adaptation in growth or metabolism? Am J Hum Biol 23(1): 65-75.
- Eregie CO (2023) Enabling the ‘Breastfeeding-Work Dyad’ and Understanding the Contextual Pentad of Productive Work, Reproductive Work, Reproductive Health, Reproductive Rights and Reproductive Politics: The Tantalizing Microcosmic Perspectives Encapsulated with Some Imaginatively Innovative Interventions. Gynecol Reprod Health 7(5): 1-16.
- Asghar W, Khalid N (2023) Nutrigenetics and nutrigenomics, and precision nutrition 29(2): 169-170.
- Eregie CO (2019) Obesity as a Public Health Emergency: A look at the ‘Pre-FOAD Hypothesis’ as a Panacea for the ‘Interventional Inequity’.
- Eregie CO (2023) The rise in diabetes burden and the compelling importance of prevention: The imperative to focus on the ‘Pre-FOAD Hypothesis’.
- Berger SL, Kouzarides T, Shiekhattar R, Shilatifard A (2009) An operational definition of epigenetics. Genes Deve 23(7): 781-783.
- Raskovalova T, Teasley SL, Gelbert Baudino N, Paola Agnese Mauri, Camille Schelstraete, et al. (2015) Breastfeeding Assessment Score: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Pediatrics135(5): e1276-e1285.
- Management of Acute Malnutrition in Infants (MAMI) Project. Chapter 7: Review of breastfeeding assessment tools. Write-up beyond the scope of the original MAMI Project and Additional Feedback from Felicity Savage and Ann Ashworth.



 We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.